what are the integers from 25 to 41
Integers
The term "integer" was adapted in Mathematics from Latin. Integer ways intact or whole. Integers are very much like whole numbers, but they also include negative numbers among them.
| 1. | What is an Integer? |
| 2. | Integers on a Number Line |
| 3. | Integer Operations |
| 4. | Addition of Integers |
| 5. | Subtraction of Integers |
| 6. | Multiplication of Integers |
| 7. | Sectionalisation of Integers |
| viii. | Rules of Integers |
| 9. | Backdrop of Integers |
| 10. | FAQs on Integers |
What is an Integer?
An integer is a number with no decimal or partial role, from the set of negative and positive numbers, including nix. Examples of integers are: -5, 0, 1, 5, viii, 97, and 3,043. A gear up of integers, which is represented as Z, includes:
- Positive Integers: An integer is positive if information technology is greater than zero. Example: 1, 2, three . . .
- Negative Integers: An integer is negative if information technology is less than zero. Example: -1, -ii, -iii . . .
- Aught is defined as neither negative nor positive integer. It is a whole number.
Z = {... -7, -6, -5, -4, -3, -ii, -1, 0, i, ii, 3, ...}

Integers on a Number Line
A number line is a visual representation of numbers on a directly line. This line is used for the comparing of numbers that are placed at equal intervals on an infinite line that extends on both sides, horizontally. Merely like other numbers, the set up of integers can also be represented on a number line.

Graphing Integers on a Number Line
Positive and negative integers can exist visually represented on a number line. Integers on a number line help in performing arithmetic operations. The basic points to continue in heed while placing integers on a number line are:
- The number on the right horizontal side is ever greater than the left side number.
- Positive numbers are placed on the right side of 0, as they are greater than "0".
- Negative numbers are placed on the left side of "0", as they are smaller than "0".
- Zero, which isn't positive or negative, is kept at the centre.
Integer Operations
The four basic arithmetic operations associated with integers are:
- Addition of Integers
- Subtraction of Integer
- Multiplication of Integers
- Division of Integers
There are some rules for doing these operations.
Before we start learning these methods of integer operations, we demand to remember a few things.
If at that place is no sign in forepart of a number, it means that the number is positive. For case, 5 means +v.
The absolute value of an integer is a positive number, i.east., |−two| = 2 and |ii| = two.
Addition of Integers
Adding integers is considered the process of finding the sum of two or more integers where the value might increase or decrease depending on the integer existence positive or negative. While adding ii integers, we come across the following cases:
- Both integers take the same signs: Add the absolute values of integers, and requite the same sign as that of the given integers to the outcome.
- Ane integer is positive and the other is negative: Observe the deviation of the absolute values of the numbers and then give the original sign of the larger of these numbers to the result.
Example: Adding ii integers: Summate the value of ii + (-v).
Solution:
Here, the absolute values of ii and (-5) are two and 5 respectively.
Their deviation (larger number - smaller number) is v - 2 = 3
At present, amongst ii and 5, 5 is the larger number and its original sign "-".
Hence, the result gets a negative sign, "-".
Therefore, 2 + (-five) = -iii
Case: Calculation ii integers: Calculate the value of -2 + v.
Solution:
Here, the absolute values of (-ii) and 5 are ii and 5 respectively.
Their difference (larger number - smaller number) is 5 - 2 = 3
At present, amidst two and 5, 5 is the larger number and its original sign "+".
Hence, the result volition exist a positive value.
Therefore,(-2) + 5 = 3
We tin can also solve the above problem using a number line. The rules for the addition of integers on the number line are:
- always showtime from "0".
- move to the right side, if the number is positive.
- movement to the left side, if the number is negative.
Permit's find the value of 5 + (-x) using a number line.
In the given problem, the outset number is 5 which is positive.
So, nosotros start from 0 and move v units to the correct side.
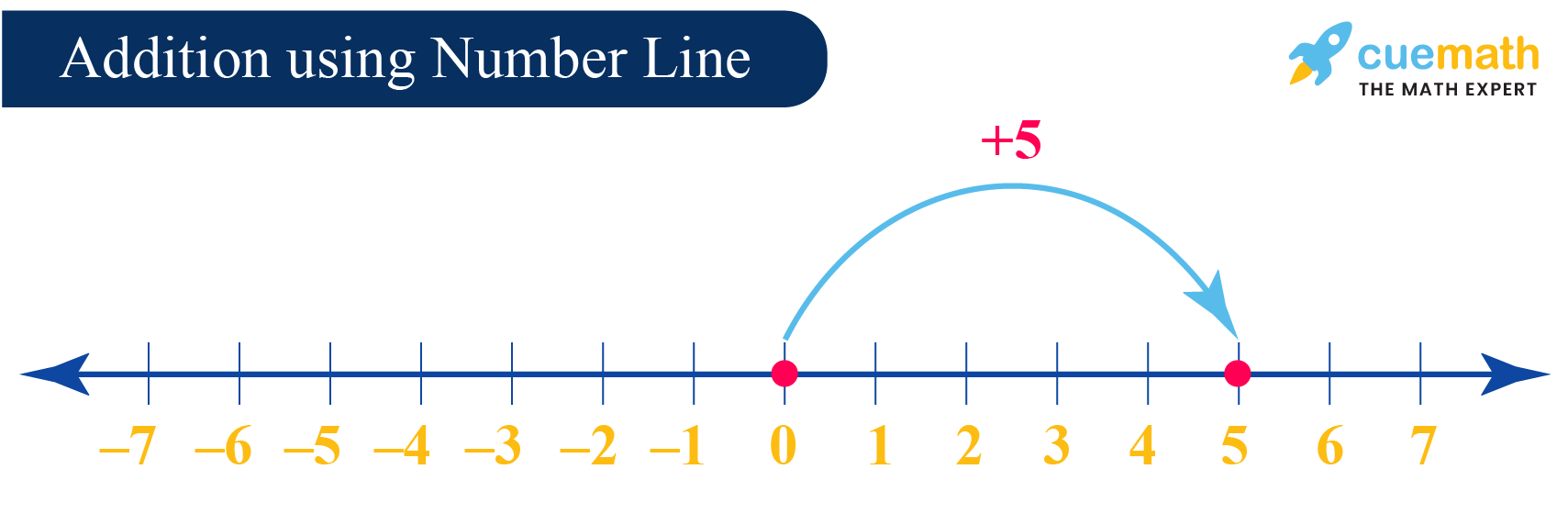
The side by side number in the given problem is -10, which is negative.
Nosotros motion (from the fifth unit) 10 units to the left side.

The number we have moved to finally is -five.
Subtraction of Integers
Subtracting integers is the process of finding the divergence between 2 or more than integers where the final value might increase or decrease depending on the integer being positive or negative. To bear out the subtraction of two integers:
- Catechumen the operation into an addition problem by changing the sign of the subtrahend.
- Apply the same rules of addition of integers and solve the problem thus obtained in the above footstep.
Example: Subtracting two integers: Calculate the value of 7 - 10.
Solution:
Converting the given expression into an addition trouble, we go: 7 + (-x).
Now, the rules for this performance will be the aforementioned as for the addition of two integers.
Here, the absolute values of vii and (-10) are seven and ten respectively.
Their difference (larger number - smaller number) is ten - 7 = 3.
At present, amid vii and ten, x is the larger number and its original sign "-".
Hence, the result gets a negative sign, "-".
Therefore, 7 - 10 = -3
Multiplication of Integers
Multiplication of integers is a similar process of repetitive add-on where an integer is added a specific number of times. To carry out the multiplication of ii integers:
- Multiply their signs and become the resultant sign.
- Multiply the numbers and add the resultant sign to the answer.
The different possible cases for the multiplication of two signs can exist observed in the following tabular array:
| Product of Signs | Result | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + × + | + | ii × 3 = 6 |
| + × - | - | two × (-3) = -6 |
| - × + | - | (-2) × three = -6 |
| - × - | + | -2 × -3 = half dozen |
Example: Multiplying integers on a number line: Calculate the value of -two × three and -2 × -iii using a number line.
Solution:
We read 2 × -3 as "ii times -3". Nosotros have to stand for -three on the number line ii times. To practise so, nosotros will start from and motion left by 3 units twice.
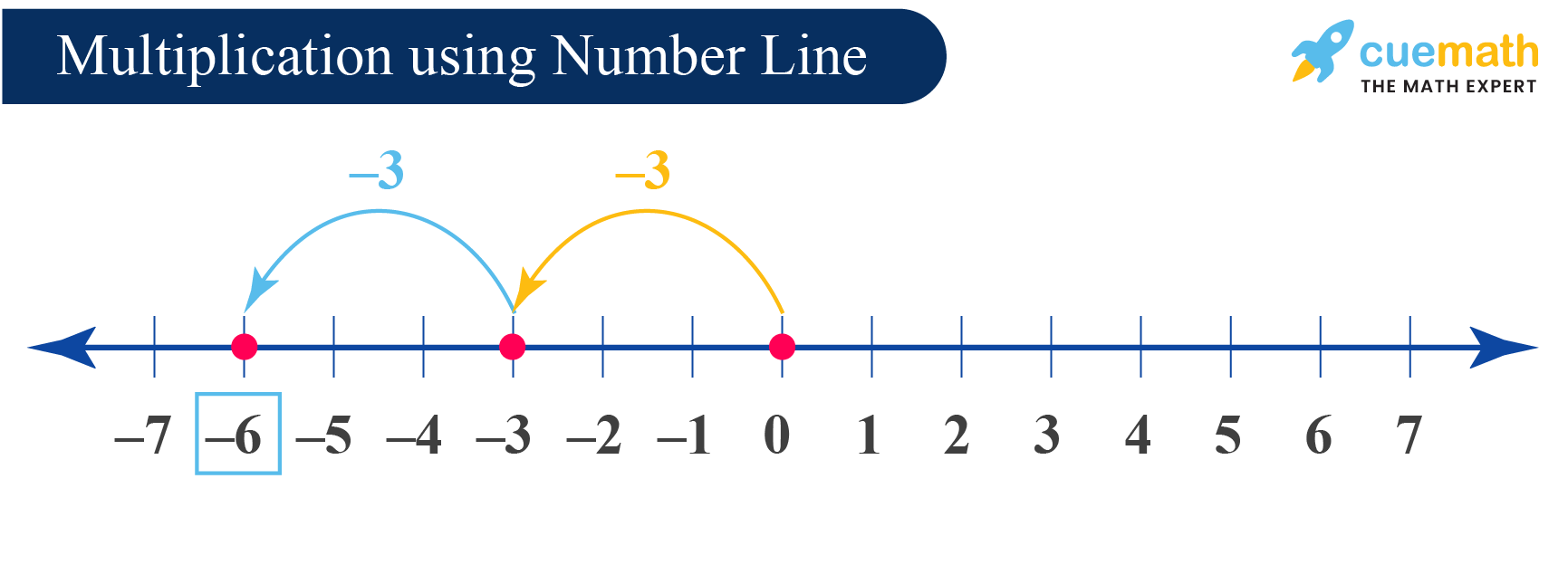
Thus, 2 × -3 = -6.
Also, -2 × -3 is like to -2 × iii, only ii is replaced past -2. Hence, we follow the same number line process as above merely in the reverse direction (i.e., to the right side).
The number line volition be represented in this way:

Therefore, -2 × -iii = 6
Partition of Integers
Division of integers means equal grouping or dividing an integer into a specific number of groups. To carry out the division functioning between two integers:
- Divide the signs of the two operands and get the resultant sign.
- Split up the numbers and add the resultant sign to the quotient.
The different possible cases for the segmentation of two signs can be observed in the post-obit table:
| Division of Signs | Event | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + ÷ + | + | 12 ÷ 3 = four |
| + ÷ - | - | 12 ÷ -3 = -4 |
| - ÷ + | - | -12 ÷ 3 = -4 |
| - ÷ - | + | -12 ÷ -3 = 4 |
Rules of Integers
Rules defined for integers are:
- Sum of two positive integers is an integer.
- Sum of ii negative integers is an integer.
- Production of two positive integers is an integer.
- Product of two negative integers is an integer.
- Addition operation between any integer and its negative value will give the issue as zero
- Multiplication operation between any integer and its reciprocal will give the result as one.
Integers Worksheets
Download integers worksheets, including addition and subtraction of integers, adding and subtracting multiple integers, and multiplication and sectionalisation of integers.
- Integers Worksheets for Form 7
- Integers Worksheets for Grade 6
- Adding and Subtracting Integers Worksheet Course five
- Adding and Subtracting Integers Worksheet Grade 7
Properties of Integers
The major Properties of Integers are:
- Closure Belongings
- Associative Property
- Commutative Property
- Distributive Property
- Additive Inverse Property
- Multiplicative Changed Property
- Identity Holding
Closure Property:
The closure property states that the gear up is closed for any particular mathematical operation. Z is closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of integers. For any two integers, a and b:
- a + b ∈ Z
- a - b ∈ Z
- a × b ∈ Z
- a/b ∈ Z
Associative Property:
According to the associative property, changing the grouping of two integers does non alter the upshot of the performance. The associative belongings applies to the addition and multiplication of two integers.
For any two integers, a and b:
- a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
- a ×(b × c) = (a × b) × c
Commutative Property:
Co-ordinate to the commutative holding, swapping the positions of operands in an functioning does non touch the result. The addition and multiplication of integers follow the commutative property.
For any ii integers, a and b:
- a + b = b + a
- a × b = b × a
Distributive Belongings:
Distributive property states that for any expression of the grade a (b + c), which means a × (b + c), operand a can exist distributed amidst operands b and c as: (a × b + a × c) i.east.,
a × (b + c) = a × b + a × c
Condiment Inverse Holding:
The additive inverse property states that the improver performance between any integer and its negative value will give the upshot every bit zero.
For any integer, a:
a + (-a) = 0
Multiplicative Changed Holding:
The multiplicative changed holding states that the multiplication operation between any integer and it's reciprocal will give the result as ane.
For any integer, a: a × 1/a = 1
Identity Belongings:
Integers follow the Identity property for add-on and multiplication operations.
Condiment identity holding states that: a × 0 = a
Similarly, multiplicative identity states that: a × 1/a = ane\
☛ Related Articles
Check now a few more than interesting articles related to integers for meliorate understanding.
- Addition and Subtraction of Integers
- Multiplication and Division of Integers
- Positive and Negative Integers Worksheets
Integers Examples
go to slidego to slidego to slide

Want to build a strong foundation in Math?
Go beyond memorizing formulas and understand the 'why' backside them. Experience Cuemath and get started.
Book a Costless Trial Class
Practice Questions on Integers
go to slidego to slide
FAQs on Integers
What Is an Integer in Math?
An integer is a number with no decimal or partial part from the set of negative and positive numbers, including zero. Examples of integers are: -5, 0, one, 5, 8, 97, and 3,043.
What Are the Different Types of Integers?
In that location are generally three types of integers:
- Positive Integers: An integer is positive if it is greater than aught. Case 1, two, three . . .
- Negative Integers: An integer is negative if information technology is less than zero. Case -1, -ii, -3 . . .
- Zero is defined as neither negative nor positive integer.
What is an Integers Formula?
The integers formula is a fix of rules followed to do the operations of integers. For each functioning, the integers formula is different. Such as for sum/difference the integers formula volition be:
- (+) + (+) = +
- (-) + (-) = -
- (+) + (-) = +
- (+) + (-) = -
For Production/ quotient the integers formula is:
- (+) × (+) = +; (+) ÷ (+) = +
- (-) × (-) = +; (-) ÷ (-) = +
- (+) × (-) = -; (+) ÷ (-) = -
- (-) × (+) = -; (-) ÷ (+) = -
☛ Also Read for Detail Understanding:
- Integer Formulas
- Consecutive Integers Formula
- Sum of Integers Formula
Can a Negative Number be an Integer?
Yes, a negative number can besides be an integer, given that it should not take a decimal or fractional role. For case: Negative numbers: -2, -234, -71, etc are all integers.
What are Consecutive Integers?
The integers that follow each other in club are called sequent integers. For example: Numbers 2,3,iv, and five are four sequent integers.
What Is the Rule for Adding a Positive and Negative Integer?
For rule for the improver of a positive and negative integer states that the divergence between the ii integers needs to be calculated in order to find their add-on. The sign of the result volition be the same as that of the larger integer of the two.
What Are Some Rational Numbers that are not Integers?
Rational numbers are those numbers that can exist represented in the \(\frac{p}{q}\) class. While some rational numbers that either have "ane" in their denominator or can be simplified to this grade, tin can be termed as Integers. Whereas, those rational numbers that cannot exist simplified to the class of fractions having "1" in their denominator, are non-integers. Rational numbers like \(\frac{2}{3}, \frac{-3}{4}, \frac{-one}{4}\),etc are not integers.
What Are the Properties of Integers?
Various arithmetic operations tin can be performed on integers, similar add-on, subtraction, multiplication and sectionalization. The major properties of integers associated with these different operations are:
- Closure Holding
- Associative Holding
- Commutative Property
- Distributive Property
- Additive Changed Holding
- Multiplicative Inverse Belongings
- Identity Holding
How Practise You Add Integers Using Estimator?
The improver of integers using a reckoner is the easiest and the quickest method to get the terminal answers. To do then bank check and endeavour Cuemath'south Adding Integers Calculator now. It adds any 2 integers and gives you the sum within a seconds. Enter whatsoever integer numbers up to two digits and press add.
☛Also Check:
- Multiplying Integers Calculator
- Subtracting Integers Calculator
- Dividing Integers Figurer
What are the applications of integers?
The awarding of positive and negative numbers in the real earth is different. They are generally used to correspond 2 contradicting situations. One common real-life awarding of integers is temperature measurement. The negative and positive numbers and zilch in the scale denote dissimilar temperature readings. Bank credit and debit statements also use integers to represent the negative or positive values of amount.
Source: https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/integers/

0 Response to "what are the integers from 25 to 41"
Post a Comment